Introduction
Specimen collection is an essential stage in medical diagnostics, ensuring accurate test results and effective patient care. Proper handling, storage, and transportation of biological samples is crucial for minimizing errors and contamination, resulting in more accurate diagnoses and treatment regimens.
Understanding Specimen Collection
Specimen collection refers to the process of obtaining biological samples, such as blood, urine, or tissue, for laboratory analysis. These samples provide crucial information about a patient's health, helping medical professionals detect diseases, monitor conditions, and evaluate treatment effectiveness.
Types of Specimens Collected
Various types of specimens are collected depending on the diagnostic requirements. Each type serves a unique purpose in medical testing.
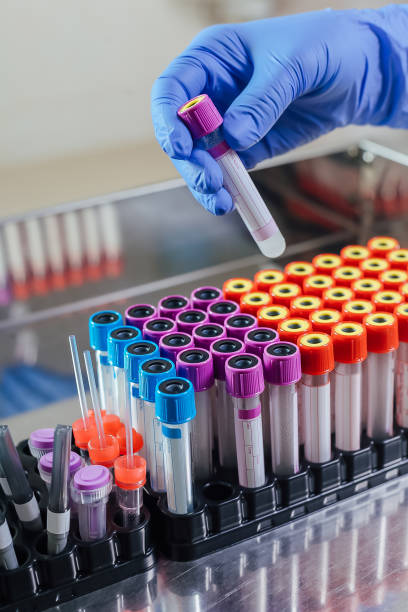
a. Blood Samples
Blood tests provide valuable insights into a patient’s overall health, diagnosing conditions such as infections, anemia, and metabolic disorders. Blood is typically drawn from veins, arteries, or capillaries using sterile needles and collected in specialized tubes for different types of analyses.
b. Urine Samples
Urine analysis helps detect kidney diseases, infections, and metabolic conditions like diabetes. Samples can be collected through random urine collection, first-morning urine, or 24-hour urine tests, depending on the medical requirement.
c. Stool Samples
Stool samples are analyzed to detect digestive system disorders, infections, and parasites. Proper collection and storage are necessary to prevent sample degradation and ensure accurate results.
d. Sputum and Saliva Samples
Respiratory specimens like sputum and saliva aid in diagnosing infections such as tuberculosis and COVID-19. These samples are collected using specialized containers and must be transported to the laboratory promptly to preserve microbial content.
e. Tissue and Swab Samples
Tissue biopsies and swabs from wounds or mucous membranes help identify infections and abnormal cell growth. Tissue samples are often collected during surgeries or minimally invasive procedures, while swabs are used for detecting bacterial or viral infections.
Best Practices for Specimen Collection
Following proper techniques in specimen collection minimizes contamination and ensures accurate test results. Healthcare professionals must adhere to strict protocols to maintain the integrity of the samples.
a. Proper Patient Identification
Correctly identifying the patient before specimen collection is essential to avoid errors and ensure test accuracy. Patients should be verified using name, date of birth, and medical record numbers before proceeding with collection.
b. Use of Sterile Equipment
Using sterile containers and tools prevents contamination and ensures reliable results. Disposable gloves, needles, and collection tubes must be handled with care and disposed of properly after use.
c. Correct Labeling and Documentation
Proper labeling and documentation help track specimens accurately and prevent mix-ups in the lab. Each sample must be labeled with patient details, collection date, and test type to ensure correct processing.
d. Handling and Storage Guidelines
Different specimens require specific storage conditions to maintain integrity before analysis. For instance, some blood samples need refrigeration, while others require immediate processing. Urine and stool samples may need preservatives to prevent bacterial overgrowth.
Challenges in Specimen Collection
Despite strict protocols, healthcare professionals face challenges such as patient cooperation, sample contamination, and handling errors. For example, hemolysis in blood samples or improper swab collection can lead to inaccurate test results, requiring recollection and delaying diagnosis.
Importance of Training and Compliance
Proper training and adherence to collection guidelines enhance the reliability of diagnostic tests and improve patient outcomes. Healthcare workers must stay updated with the latest best practices, use standardized procedures, and follow regulatory requirements to minimize errors and enhance laboratory efficiency.
Conclusion
Specimen collection is an essential step in medical diagnostics, and following best procedures assures accurate results and improved healthcare decisions. Healthcare workers that use effective gathering strategies can deliver reliable diagnostic data, thereby enhancing patient treatment and outcomes. Accurate specimen handling is more than just a laboratory requirement; it is an essential component of providing successful medical treatment.
Comments on “The Essential Guide to Specimen Collection”